What Are Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs)?
As India continues its digital transformation, one set of tools stands out in making everyday transactions quicker, easier, and more accessible: Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs). These instruments allow users to load funds in advance and use them for a wide range of payments—without needing physical cash or traditional banking tools.
PPIs are digital alternatives that come in various formats like prepaid cards, mobile wallets, and electronic vouchers. They can be used to shop online or offline, pay utility bills, book travel, transfer money, or even receive government subsidies. Whether someone lives in a metropolitan city or a remote village, PPIs have become a practical solution for engaging with the growing digital economy.
Read Article: Digital Lending Guidelines in India: What Fintech Startups Must Follow
How Do Prepaid Payment Instruments Work?
A Prepaid Payment Instrument is essentially a financial tool that stores value digitally. Users deposit money into the instrument (via a card, bank account, or wallet), which is then available for various types of payments.
Key Characteristics of PPIs:
- Preloaded Funds: Users load money into the instrument before making a purchase.
- Digital Format: PPIs are available digitally and can be accessed through apps, cards, or SMS-based services.
- Transaction Recording: Every payment is digitally recorded for tracking and security purposes.
- Reloadable vs. One-Time: Some PPIs can be used multiple times, while others are designed for single-use.
- Merchant Acceptance: Usability depends on the instrument type and merchant network.
Real-World Applications of PPIs
PPIs are now part of everyday life. Here are some of the common ways people use them:
- Buying products from online and offline stores
- Paying electricity, gas, and water bills
- Recharging mobile phones or DTH services
- Booking bus, train, or flight tickets
- Transferring money to others (depending on KYC)
- Managing company or employee expenses
- Disbursing government welfare schemes
- Receiving promotional offers and cashback rewards
These use cases demonstrate the versatility of PPIs and why they’ve become so widespread.
The Regulatory Role of the RBI
The Reserve Bank of India(RBI) is the key regulator of PPIs. Its job is to ensure that these instruments function safely and transparently, protecting consumers and promoting financial innovation at the same time.
Regulatory Responsibilities Include:
- Issuing licenses for PPI providers under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007
- Defining security standards and compliance guidelines
- Monitoring usage limits, KYC norms, and interoperability rules
- Enforcing customer protection mechanisms like grievance redressal
To issue PPIs in India, companies must secure approval from the RBI and comply with multiple operational and financial requirements, including maintaining minimum capital and following cybersecurity norms.
KYC Norms and Transaction Limits
The type of Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance a user has completed determines how the PPI can be used:
- Minimum KYC PPIs: Monthly usage is limited to ₹10,000. These are ideal for new or casual users.
- Full KYC PPIs: Offer higher transaction limits, fund transfer capabilities, and interoperability with other wallets or bank accounts.
- Reload and Withdrawal Limits: Depend on the PPI type and user verification.
These rules ensure both security and flexibility in the payment ecosystem.
Types of PPIs in India
The RBI classifies PPIs into three main categories:
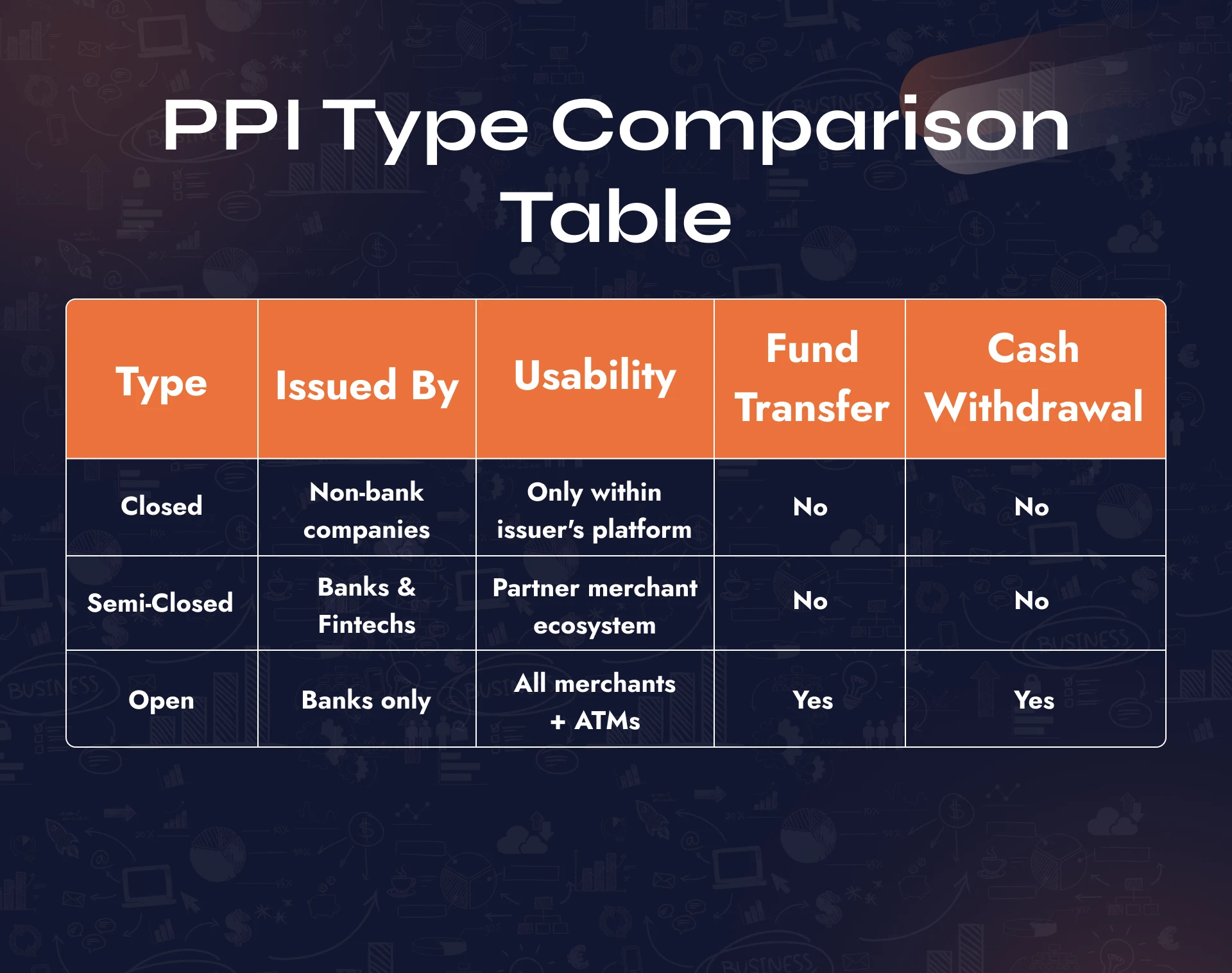
Closed System PPIs
These are issued by companies for use within their own platforms. Users cannot withdraw money or use the balance elsewhere.
Examples:
- Amazon Gift Cards
- Ola Money
- BookMyShow Wallet
Use Cases:
- Making purchases or payments within the app
- Receiving cashback or promotional credits
- Gifting prepaid value to others
Limitations:
- Cannot transfer funds to bank accounts or use across multiple vendors
Semi-Closed System PPIs
These instruments can be used at multiple but restricted merchants who have an agreement with the issuer. They’re more flexible than closed PPIs but do not allow cash withdrawal.
Examples:
- Paytm Wallet
- PhonePe Wallet
- MobiKwik
Use Cases:
- Online and offline purchases at affiliated stores
- Bill payments and mobile/DTH recharges
- Booking tickets and making merchant payments
Limitations:
- No cash withdrawal
- Usage limited to network of partner merchants
Open System PPIs
These are the most flexible PPIs and are issued only by banks. They enable spending at any merchant that accepts cards, ATM withdrawals, and fund transfers.
Examples:
- ICICI Pockets
- SBI Prepaid Card
- HDFC Forex Card
Use Cases:
- Shopping at physical and digital stores
- Withdrawing cash from ATMs
- Transferring funds to other bank accounts
Benefits:
- Broad usability
- Full KYC-based features
- More like a debit card in function
PPI Type Comparison Table
Benefits of Using PPIs
PPIs offer a number of practical advantages, making them increasingly popular:
Convenient Payments
Paying through digital wallets or prepaid cards is faster and more seamless than using cash or even bank accounts.
Financial Inclusion
Anyone with a mobile phone can use PPIs—even those who don’t have a traditional bank account.
Enhanced Security
Features like OTP authentication, transaction tracking, and encryption help protect users.
Controlled Spending
With a prepaid balance, users can better manage their spending and avoid overspending.
Cashback and Rewards
Many PPI issuers incentivize usage through discounts, cashback offers, or loyalty points.
Challenges and Limitations
While PPIs are immensely useful, they come with some drawbacks:
Limited Acceptance
Closed and semi-closed wallets are only accepted at select outlets or platforms.
Cap on Transactions
Spending limits based on KYC level may restrict usage for high-volume users.
Expiry Dates
Some PPIs have expiration periods. Unused funds may lapse if not redeemed.
No Interest on Balance
Unlike savings accounts, the money held in PPIs doesn’t earn interest.
Latest Trends and Developments
Digital Inclusion Initiatives
Programs like Digital India and Jan Dhan Yojana have introduced millions to formal finance, helping drive PPI adoption.
UPI Integration
Popular wallets now offer UPI-based payments for even more flexibility and ease of use.
Push for Interoperability
The RBI now requires full-KYC PPIs to be interoperable—allowing users to transact across platforms and send money to bank accounts or other wallets.
Rise of Fintech Innovation
Fintech startups are entering the PPI market with creative solutions like employee expense cards, student wallets, travel cards, and more.
Why PPIs Are Crucial for India’s Payment Ecosystem
PPIs are an essential part of India’s cashless revolution. They bridge the gap between those with full access to banking services and those still entering the digital world. Their utility, low entry barrier, and versatility make them key to achieving financial inclusion.
From microtransactions to corporate expense management, PPIs provide practical value across many segments. For regulators and innovators alike, the growth of this sector is a sign of a more digitally connected India.
Final Thoughts: A Growing Opportunity for Fintechs and Institutions
Prepaid Payment Instruments are no longer just a convenience—they are a foundation for modern payments in India. Their ability to serve unbanked individuals, support e-commerce, and simplify everyday financial transactions makes them indispensable.
As an NBFC Advisory, we encourage fintech startups, NBFCs, and financial institutions to explore the possibilities in this space. By developing compliant, secure, and user-friendly PPI products, businesses can unlock vast potential and contribute meaningfully to India’s financial ecosystem.
To learn more about licensing, compliance, or launching your own PPI product, refer to the official RBI PPI portal.
Our Article: Fintech-NBFC Partnerships: Opportunities & Challenges in India’s Digital Finance