Inside This Article
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) play an essential role in the Indian financial system by offering credit, loans, and investment options. However, the incorporation of an NBFC is only the first step. To ensure regulatory compliance and smooth business operations, NBFCs must follow several post-incorporation requirements set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), and other regulatory authorities.
In this blog, we’ll cover:
- Why post-incorporation compliance is essential for NBFCs.
- Key regulatory requirements for NBFCs.
- Challenges in managing compliance effectively.
- Best practices to ensure seamless adherence to compliance norms.
Why Post-Incorporation Compliance is Essential for NBFCs?
The Challenge:
NBFCs must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to remain operational. Failing to comply can result in penalties, damage to reputation, and even the cancellation of the NBFC license.
Key issues include:
● Stringent RBI guidelines for financial stability.
● Need for robust governance and risk management.
● Compliance with multiple regulatory bodies.
The Solution:
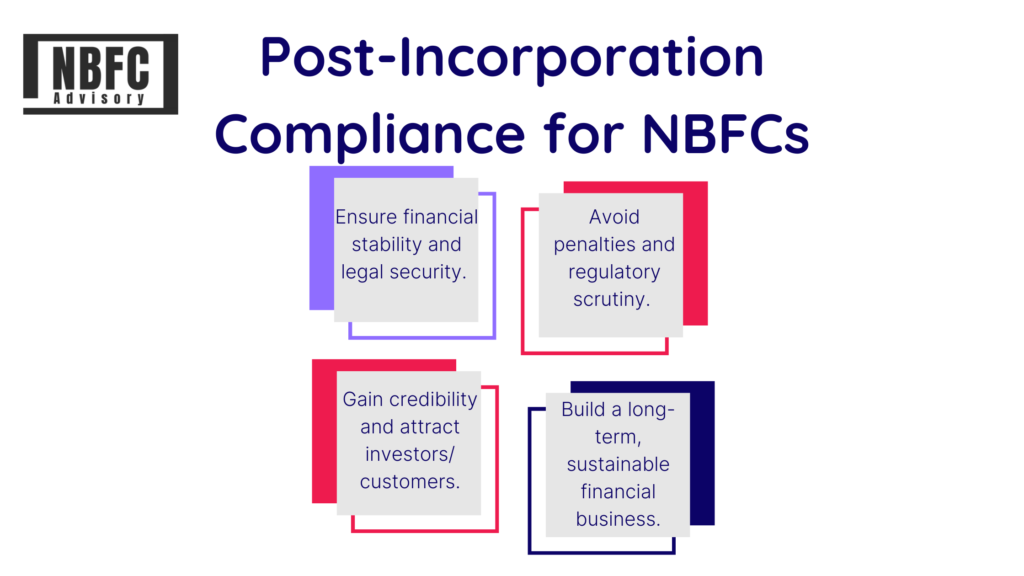
By adhering to regulatory compliance requirements, NBFCs can:
- Ensure financial stability and legal security.
- Avoid penalties and regulatory scrutiny.
- Gain credibility and attract investors/customers.
- Build a long-term, sustainable financial business.
Key Post-Incorporation Compliances for NBFCs
RBI Compliance Requirements
Obtain NBFC Registration Certificate:
- Apply for an NBFC license under Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, 1934.
- Maintain a minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) of ₹2 crores (₹5 crores for NBFC-MFIs and NBFC-IFCs).
Fair Practices Code (FPC) Implementation:
- Develop and publish an FPC document to ensure fair and transparent lending practices.
- Display the FPC on the website and provide copies to customers upon request.
Annual & Periodic RBI Filings:
- Submit NBS-1 (quarterly financial statements) and NBS-2 (quarterly Prudential Norms compliance report).
- File NBS-9 (annual return for NBFCs with assets < ₹500 crores).
- Submit a Statutory Auditor Certificate (SAC) confirming compliance.
KYC & AML Compliance:
- Implement Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies as per RBI guidelines.
- File Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) with FIU-IND if necessary.
Asset-Liability Management (ALM) Policy:
- NBFCs must maintain an Asset-Liability Management (ALM) Policy and submit reports based on their asset size.
MCA Compliance Requirements
Board Meetings & General Meetings:
- Conduct the first board meeting within 30 days of incorporation.
- Hold at least four board meetings annually.
- Conduct an Annual General Meeting (AGM) within six months after the end of the financial year.
Statutory Filings with MCA:
- File Form AOC-4 (financial statements) and Form MGT-7 (annual return) yearly.
- File DIR-3 KYC for all directors annually.
Appointment of Statutory Auditors:
- Appoint an RBI-registered auditor and submit an Annual Statutory Auditor Certificate (SAC) confirming compliance.
GST and Tax Compliance
GST Registration and Returns:
- NBFCs providing financial services must register under the GST Act.
- File GSTR-1 (outward supplies) and GSTR-3B (monthly tax summary).
Income Tax Compliance:
- File annual Income Tax Returns (ITR-6).
- Deduct Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on interest payments and file quarterly TDS returns (Form 26Q).
Challenges in Compliance for NBFCs
Complex Regulatory Framework
- Multiple regulatory bodies (RBI, MCA, SEBI, FIU-IND) create compliance complexity.
- Frequent amendments in RBI norms require constant monitoring.
High Cost of Compliance
- Costs include audit fees, compliance software, legal consultations, and internal monitoring teams.
Cybersecurity & Data Protection
- NBFCs manage sensitive customer data and must ensure robust IT security.
- Compliance with data protection laws is critical to prevent breaches.
Capital Adequacy & Liquidity Management
- RBI mandates that NBFCs maintain Capital to Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) of at least 15%.
- Managing liquidity while remaining compliant is a challenge.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance
Develop a Strong Compliance Culture
- Appoint a Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) to oversee regulatory compliance.
- Conduct regular compliance training for employees.
Leverage Technology for Compliance Management
- Use RegTech solutions to automate regulatory reporting.
- Implement cloud-based compliance tracking tools.
Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes
- Subscribe to RBI/MCA notifications and attend industry seminars.
- Engage with NBFC advisory firms for compliance consultation.
Final Thoughts
Staying compliant is not just a legal obligation; it is essential for long-term sustainability and credibility in the financial market. NBFCs that prioritize regulatory compliance will gain a competitive edge, avoid penalties, and build customer trust. Need expert guidance on NBFC compliance? Contact an NBFC advisory Team today!
📞 Call Us: +91 93287 18979 | 🌐 Visit: nbfcadvisory.com