Inside This Article
Introduction
Around the world, the COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly affected people’s comfort levels with digital technology. The ‘new normal’ of payment reached 70 billion transactions in 2022, which was 44 billion in 2021.
This has created opportunities for new entrepreneurs and small businesses. And finding the right method of the payment transaction is a vital part of any business.
However, many business owners are unfamiliar with many digital payment processes — including payment gateways, payment aggregators, and related compliance.
In this blog, we have compiled common questions about payment aggregators VS payment gateways. To better understand with minimum hassle, let’s read on further!
Payment Aggregator VS Payment Gateway
Meaning
A payment aggregator (also known as a merchant aggregator or payment service provider) offers merchants a variety of payment options. It allows online payments (UPI card, etc.), offline payments, cash, and cheque. Example: Bill Desk, PayUMoney, etc.
A payment gateway is a payment software that allows the safe and secure transfer of money from the customer’s bank account to the merchant’s bank. Unlike payment aggregators, a payment gateway allows only specific payments listed on a portal. Examples: HDFC, Razorpay, ICICI, etc.
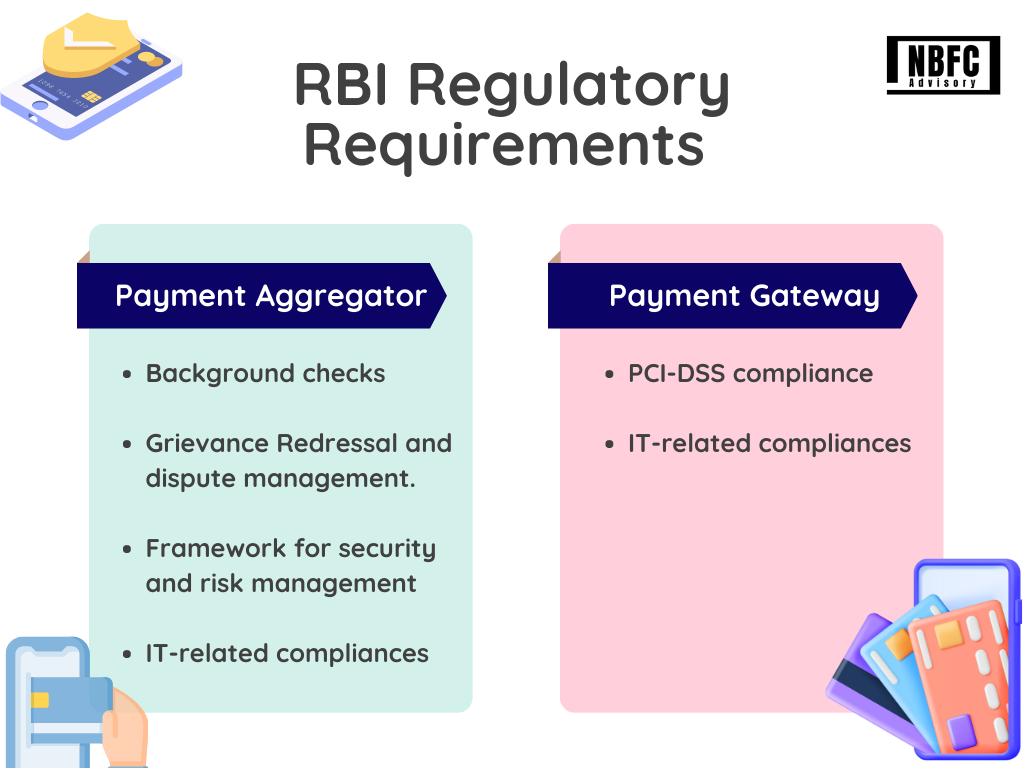
RBI regulatory requirements and compliance for Payment Aggregator and Payment Gateway
Payment Aggregator
1. Background checks
According to the Reserve Bank of India’s “Master Direction – Know Your Customer (KYC) Directions,” Payment Aggregators need to follow KYC, AML, and CFT regulations.
To ensure that merchants have no illegal intentions of duping customers or selling fake/counterfeit/prohibited products, payment aggregators must conduct background and antecedent checks on them. According to the RBI Guidelines, payment aggregators are also required to verify that merchants’ websites contain appropriate terms and conditions.
Moreover, the guidelines specify that payment aggregators must ensure that on-boarded merchants’ infrastructure meets both Payment Card Industry-Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) and Payment Application-Data Security Standard (PA-DSS) compliance.
2. Grievance Redressal and dispute management
Guidelines by the RBI mandate that payment aggregators establish a formal and open dispute management and grievance redressal process for their customers.
The Payment Aggregator should appoint a nodal officer who will handle any customer complaints/grievances & the escalation matrix. In addition, all participants in the transaction would be bound by the dispute resolution mechanism.
3. Framework for security and risk management
According to the RBI guidelines, the following are mandatory:
- Submission of the system audit report, including the cyber security audit conducted by the CERT-In, impaneled auditors. Care should be taken to perform this audit two months before the financial year ends in the regional office, DPS, and RBI.
- Cyber security incidents and breaches must be monitored, handled, and reported to DPSS, RBI Central Office Mumbai, and CERT-In.
- Payment System Operators must follow data storage requirements.
- Implementation of a risk mitigation strategy for information security.
- To prevent and detect fraud, there is a need for an adequate information and data security infrastructure.
4. IT-related compliances
Some of the requirements for IT systems and security are as follows:
- Applying the data security standards such as PCI-DSS, PA-DSS, etc.
- Reporting and submission of monthly cyber security incidents/cardholder data breaches with analysis to the RBI.
- Attention to security assessments while onboarding a merchant.
- The following audit reports must conduct and submit to the IT committee: quarterly internal audits, annual external audits, biannual vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, PCI-DSS attestations, and ROC compliance reports.
Payment Gateway
1. PCI-DSS compliance
It includes the following compliances:
- Physical restrictions on access to cardholder data.
- Timely update of the software.
- Vulnerability scanning and testing.
- Updating and maintaining anti-virus software.
- Firewall installation and maintenance.
- Protection of password and cardholder data.
- Creating unique IDs to access restricted data.
2. IT-related compliances
This is similar to the payment aggregators, which include data security standards, reporting security incidents, onboarding of merchants, cyber security audits & reports, etc.
Pros and cons of payment aggregator and payment gateway – and Suitability

Payment Aggregators
Pros
- Due to the cost-effective and simple fee structure, it is suitable for large volumes of smaller transactions. It also helps the merchants to understand the amount needed for the processing fees.
- With minimal paperwork and compliance check, payment aggregators provide ease of application and immediate processing of payments.
- The quick and easy setup encourages new businesses in the market.
Cons
- Higher possibility of account holds – Your account might be on hold if any payment activity on your website suspects fraud. Although hold times are usually shorter than 24 hours, they may last up to a month in exceptional cases. These interruptions are less likely to occur with individual merchant accounts.
- Most aggregators will hold your fund from 1-3 days to 30 days. Since they are responsible for their monthly fees, if they need to float your money, they will. This is not a common scenario, so it’s best to ask these questions.
Payment Gateway
Pros
- Secures sensitive information for stress-free digital transactions.
- A simple user interface and a faster transaction process.
- Expand the customer base by accepting payment and currency conversions worldwide.
Cons
- Problems with technical aspects can take a maximum amount of time to resolve.
- The gateway or user bank charges a merchant fee whenever there are credit purchases.
- Fixed fee per month or transaction.
Do you need both Payment Aggregator and Payment Gateway?
There are two common myths:
- Payment aggregator and Payment gateway are interchangeable.
- A gateway is enough for payment processing.
You cannot choose one over the other!
The payment gateway takes care of the technical side, i.e., transaction data and payment aggregators are the interfaces themselves — and both are complementary. Each of them collaborates with banks working on the back end to create merchant accounts. The authorized banks will have to arrange both the underwriting and fund transfer process when multiple merchants apply for merchant accounts and want to process payments.
This is where the payment aggregator handles the underwriting process with the acquiring bank and allows the processing of payments for the merchants.
The bottom line: Any business requiring online transactions can enjoy both. Some industries that use both PA and PG include agency owners, B2B/B2C, service providers, and software services, to name a few.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a payment gateway and a payment service provider?
Payment gateways usually serve two purposes during a transaction: at the beginning & end, where end-users provide card details & receive consent or rejection.
A payment processor processes the information between the consumer’s bank and the merchant acquirer until the transaction is complete.
2. How does Payment aggregator & Payment gateway help small businesses?
Payment aggregators are suitable for micro-transactions. The merging of payment gateways and aggregators allows small businesses to quickly access payment transactions. With low or no startup costs, Payment Aggregators offer online transaction processing.
3. Define PCI-DSS Compliance.
PCI-DSS Compliance refers to a set of requirements created to ensure the security of credit card data processing, storage, and transmission in a secure environment.
4. What is a payment aggregator license?
By using aggregators, merchants can accept credit cards and bank transfers without opening a merchant account. To do this, a Payment aggregator needs to get a payment aggregator license to provide diverse payment options.
How we can help!
It must be clear that the payment gateway serves as an interface for accepting online payments, not processing them. But, the Payment aggregator connects various payment gateways under one digital roof, facilitating multiple payment options, including UPI, debit/credit cards, etc.
We at NBFC Advisory, with more than 8 years of experience — our team of professionals will plan your next move to set up your payment system.
Suppose you want to be amongst the next big financial businesses. NBFC Advisory has you covered for an overall digital business setup.





